개요
Kubernetes 클러스터를 생성하고 Helm 차트를 통해 다양한 애플리케이션을 설정하다 보면 볼륨에 대한 설정이 항상 등장합니다. 이러한 상황에서 볼륨에 대해서 자세히 모르다 보면 이 부분에서 헤매는 경우가 종종 발생하게 되고 급하게 많이 사용하는 csi-driver 나 longhorn 등을 설치해서 문제를 해결하곤 합니다.
그런데 여기서 csi-driver는 실제로 어떻게 구성되고 동작할까요? 우리는 보통 설치하고 문제없이 동작하는 것을 확인하지만 내부에서 어떤 방식을 이용해서 동작하는지는 문제가 생겼을 때 확인해 보곤 합니다. 좀 더 자세히 공부해 보자는 의미에서 본 글에선 여기서 CSI는 무엇이고 어떤 구성요소들이 있는지에 대해서 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
CSI
Kubernetes v1.9부터 컨테이너 스토리지 인터페이스(Container Storage Interface, CSI)가 알파 버전으로 지원되기 시작했습니다. v1.10에서 베타 버전으로 지원되었고, v1.13에서 GA가 되었습니다.
Kubernetes의 스토리지 관련 기능은 Kubernetes 소스에 직접 내장된 구현(“in-tree”)으로만 제공되었습니다. 따라서 외부 스토리지를 개발하는 3rd party 벤더는 Kubernetes 소스 코드에 업스트림을 해야 했고, Kubernetes 개발팀과 릴리스 시기를 맞춰야 한다는 문제가 있었습니다. 중간에 v1.8에서 추가된 Flex-volume이라는 플러그인 기반 솔루션이 API를 노출하여 문제를 해결하려고 시도했습니다. 하지만 몇몇 문제점들이 존재하여 넓게 이용되지 못했습니다.
Flex-volume 솔루션은 k8s 바이너리를 분리한다는 측면에서 CSI와 유사한 원칙에 따라 동작하지만, 이 접근 방식에는 여러 가지 문제가 있었습니다. 첫째, 드라이버 파일을 배포하려면 마스터 및 호스트 파일 시스템에 대한 루트 액세스 권한이 필요했습니다. 둘째, 호스트에서 사용할 수 있다고 가정한 운영 체제 종속성 및 전제 조건이 상당히 부담스러웠습니다.
이러한 문제를 해결하고자 Kubernetes에서는 CSI를 지원함으로써 Kubernetes 소스에 포함하지 않고 3rd party 벤더가 자체적으로 구현할 수 있는(“out-of-tree”) 방식으로 제공할 수 있게 되었습니다. 또한, Kubernetes에서 기존에 제공하던 StorageClass, PersistentVolume, PersistentVolumeClaim을 CSI에서도 계속 사용할 수 있어, 컨테이너를 배포하고자 하는 사용자 입장에서는 v1.8 이전과 동일한 조작으로 CSI를 통해 외부 스토리지를 이용할 수 있게 되었습니다.
이 CSI는 Kubernetes, Mesos, Docker, CloudFoundry 등 다양한 컨테이너 환경에서 사용할 수 있도록 Kubernetes와 독립적으로 Container Storage Interface 커뮤니티에서 사양을 수립하고 있습니다.
CSI Driver 메커니즘
먼저 전반적으로 CSI 드라이버들이 어떻게 동작하는지 알기 위해서 Kubernetes에서 권장하는 메커니즘에 대해서 설명하도록 하겠습니다.
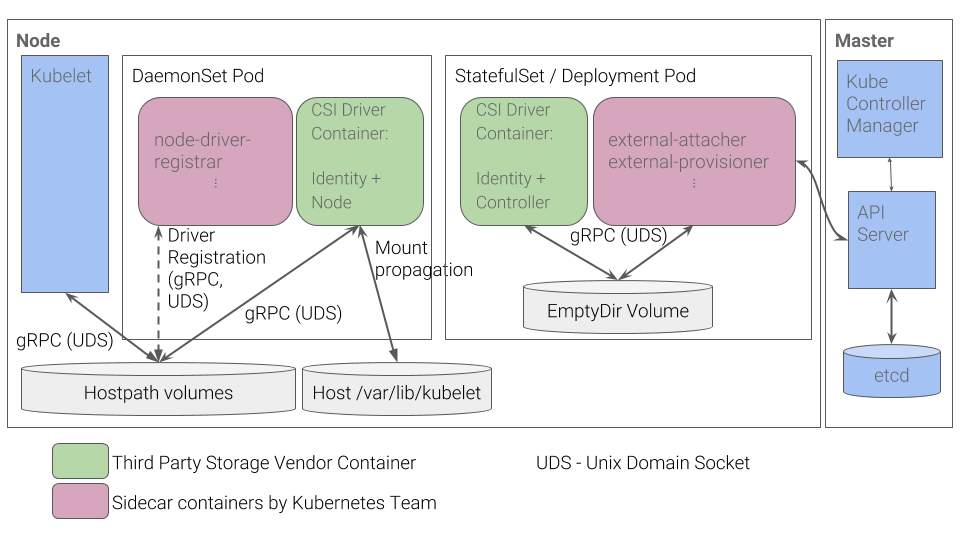
Kubernetes는 3rd party 벤더들이 CSI 볼륨 드라이버를 만들 때 다음과 같은 사항을 따르는 것을 권장합니다.
- 볼륨 플러그인 동작을 구현하고 CSI 사양(컨트롤러, 노드 및 신원 서비스 포함)에 정의된 대로 유닉스 도메인 소켓을 통해 gRPC 인터페이스를 노출하는 “CSI volume driver” 컨테이너를 만듭니다.
- “CSI volume driver“에 Kubernetes 팀이 지원할 헬퍼 컨테이너를 번들합니다. (external-attacher, external-provisioner, node-driver-registrar, cluster-driver-registrar, external-resizer, external-snapshotter, livenessprobe). 이러한 헬퍼 컨테이너는 드라이버가 Kubernetes 시스템과 상호작용 하는 것을 돕습니다. 이러한 헬퍼 컨테이너에 대한 자세한 내용은 아래에서 설명하도록 하겠습니다.
- 클러스터 관리자가 위 다이어그램의 StatefulSet과 DaemonSet을 배포하여 클러스터에 스토리지 시스템에 대한 지원을 추가하도록 합니다.
여기서 모든 구성 요소(
external-provisioner와external-attacher를 포함한)를 단일 Pod에 배치하여 배포를 단순화할 수도 있습니다. 하지만 이렇게 구성할 경우, 더 많은 리소스가 소모되고external-provisioner및external-attacher구성 요소에 리더 선출 프로토콜(예 : https://github.com/kubernetes-retired/contrib/tree/master/election)이 필요합니다.
Components of CSI Driver
Controller Component
컨트롤러 플러그인은 Deployment 또는 StatefulSet으로 배포되며 클러스터 내의 모든 노드에 마운트 할 수 있습니다. 이는 CSI Controller 서비스를 구현하는 CSI 드라이버와 사이드카 컨테이너로 구성됩니다. 컨트롤러 사이드카 컨테이너는 일반적으로 쿠버네티스 오브젝트와 상호 작용하고 CSI Controller 서비스를 호출합니다.
컨트롤러는 호스트에 직접 액세스 할 필요가 없습니다.(외부 컨트롤 플레인 서비스와 쿠버네티스 API를 통해 모든 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.) 고가용성(HA)을 위해 컨트롤러 구성 요소의 복사본을 여러 개 배포할 수 있지만, 리더 선출을 구현하여 특정 시간에 하나의 컨트롤러만 활성화되도록 해야 합니다.
Sidecar Containers
CSI 사이드카 컨테이너는 쿠버네티스에서 CSI 드라이버의 개발 및 배포를 간소화하는 것을 목표로 하는 표준 컨테이너 세트입니다. 이러한 컨테이너에는 Kubernetes API를 감시하고, “CSI 볼륨 드라이버” 컨테이너에 대해 적절한 작업을 트리거하고, 적절하게 Kubernetes API를 업데이트하는 공통 로직이 포함되어 있습니다.
여기서 설명하는 사이드카 컨테이너는 다음과 같은 컨테이너들이 포함되어 있습니다.
- external-provisioner
- external-attacher
- external-snapshotter
- external-resizer
- node-driver-registrar
- cluster-driver-registrar (deprecated)
- livenessprobe
아래는 추가적인 설정 없이 ebs-csi-driver를 설치했을 때 Deployment로 생성된 ebs-csi-controller의 내용입니다. 위의 provisioner, attacher, snapshotter, resizer 및 liveness-probe가 포함되어 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
> k get po -n kube-system ebs-csi-controller-67bbddfc9-6f8vt -o yaml | yq e '.spec.containers.[].name'
ebs-plugin
csi-provisioner
csi-attacher
csi-snapshotter
csi-resizer
liveness-probe
Per-node Component
노드 플러그인은 DaemonSet을 통해 클러스터의 모든 노드에 배포해야 합니다. 이는 CSI Node Service를 구현하는 CSI Driver와 node-driver-registrar 역할을 하는 사이드카 컨테이너로 구성됩니다.
이 컴포넌트는 모든 노드에서 실행되며 kubelet과 통신하며 CSI Node service에 대한 요청을 처리합니다. 이러한 호출은 스토리지 시스템에서 스토리지 볼륨을 Mount 혹은 Unmount 하며 그것들을 Pod가 이용할 수 있도록 해줍니다. kubelet은 호스트의 HostPath 볼륨을 통해 공유되는 UNIX domain socket을 사용하여 CSI driver를 호출합니다. 추가적인 UNIX domain socket은 node-driver-registrar이 드라이버를 kubelet에 등록하는 데 사용됩니다.
아래는 ebs-csi-driver를 설치했을 때 DaemonSet으로 생성된 ebs-csi-node의 내용입니다. 위의 설명처럼 node-driver-registrar에 HostPath 볼륨이 연결되어 있으며 csi.sock를 사용하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
> k describe po -n kube-system ebs-csi-node
Volumes:
kubelet-dir:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /var/lib/kubelet
HostPathType: Directory
plugin-dir:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /var/lib/kubelet/plugins/ebs.csi.aws.com/
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
registration-dir:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /var/lib/kubelet/plugins_registry/
HostPathType: Directory
device-dir:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /dev
HostPathType: Directory
probe-dir:
Type: EmptyDir (a temporary directory that shares a pod's lifetime)
Medium:
SizeLimit: <unset>
...
Containers:
...
node-driver-registrar:
...
Requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 40Mi
Liveness: exec [/csi-node-driver-registrar --kubelet-registration-path=$(DRIVER_REG_SOCK_PATH) --mode=kubelet-registration-probe] delay=30s timeout=15s period=90s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment:
ADDRESS: /csi/csi.sock
DRIVER_REG_SOCK_PATH: /var/lib/kubelet/plugins/ebs.csi.aws.com/csi.sock
Mounts:
/csi from plugin-dir (rw)
/registration from registration-dir (rw)
/var/lib/kubelet/plugins/ebs.csi.aws.com/ from probe-dir (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-kz76w (ro)
노드 플러그인은 드라이버 볼륨을 마운트 하기 위해 호스트에 직접 액세스해야 합니다. 파일 시스템 마운트와 Block Device를 kubelet에서 사용할 수 있게 하려면, CSI 드라이버는 드라이버 컨테이너가 생성한 마운트를 kubelet이 볼 수 있도록 하는 양방향 마운트 포인트를 사용해야 합니다.
Unix Domain Socket(UDS)란 IPC socket(inter-process communication socket) 이라고도 하며 TCP의 소켓과 동일한 API로 데이터를 주고받을 수 있는 local file 기반의 소켓입니다. 더 자세한 내용은 Reference의 [유닉스 도메인 소켓(Unix Domain Socket) 이란?]을 참고해 주세요.
트러블슈팅
마침 테스트 환경에서 Persistent Volume을 삭제하려는데 원인을 알 수 없는 문제를 보게 되어서 트러블 슈팅 과정을 정리해 보았습니다.
이슈
기존에 테스트에서 사용하던 Persistent Volume(이하 PV)을 삭제하려는데 Terminating 상태에서 멈춰있는 현상이 발생했습니다.
원인을 파악하고자 PV를 describe 했더니 다음과 같은 결과를 볼 수 있었습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
> k describe pv pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720
Name: pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720
Labels: <none>
Annotations: pv.kubernetes.io/provisioned-by: ebs.csi.aws.com
volume.kubernetes.io/provisioner-deletion-secret-name:
volume.kubernetes.io/provisioner-deletion-secret-namespace:
Finalizers: [external-attacher/ebs-csi-aws-com]
StorageClass: ebs-sc
Status: Terminating (lasts 11m)
Claim: default/ebs-claim
Reclaim Policy: Delete
Access Modes: RWO
VolumeMode: Filesystem
Capacity: 10Gi
Node Affinity:
Required Terms:
Term 0: topology.ebs.csi.aws.com/zone in [ap-northeast-2a]
Message:
Source:
Type: CSI (a Container Storage Interface (CSI) volume source)
Driver: ebs.csi.aws.com
FSType: ext4
VolumeHandle: vol-0de988bf2cd660fc4
ReadOnly: false
VolumeAttributes: storage.kubernetes.io/csiProvisionerIdentity=1709191946455-2302-ebs.csi.aws.com
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning VolumeFailedDelete 11m (x7 over 12m) ebs.csi.aws.com_ebs-csi-controller-67bbddfc9-zchxr_6c064a65-efaa-44ed-ba6d-08c3a0812ea0 persistentvolume pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720 is still attached to node ip-10-29-76-202.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal
여기서 이벤트 정보만 보았을 때는 원인이 무엇인지 알기 어려웠습니다. 그래서 CSI Driver의 동작 방식을 참고하여 조사해 보았습니다.
Digging
먼저 Reference의 [CSI - Spec]을 참고하여 스펙 및 Volume의 Lifecycle을 확인해 보았습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
CreateVolume +------------+ DeleteVolume
+------------->| CREATED +--------------+
| +---+----^---+ |
| Controller | | Controller v
+++ Publish | | Unpublish +++
|X| Volume | | Volume | |
+-+ +---v----+---+ +-+
| NODE_READY |
+---+----^---+
Node | | Node
Publish | | Unpublish
Volume | | Volume
+---v----+---+
| PUBLISHED |
+------------+
Figure 5: The lifecycle of a dynamically provisioned volume, from
creation to destruction.
해당 링크의 Volume Lifecycle 부분을 참고하면 당연하겠지만 삭제 시 DeleteVolume 작업이 이루어진다는 것 그리고 해당 작업에 대한 RPC Interface가 정의되어 있다는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
그다음 메커니즘의 그림에서 DaemonSet Pod가 볼륨을 컨트롤한다는 것을 확인할 수 있었으므로 Reference의 [Kubernetes CSI Sidecar Containers]에서 Sidecar Container 중 어떤 컨테이너가 해당 작업을 하는지 확인하고자 했습니다.
그리고 external-provisioner의 설명에서 다음과 같은 내용을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
The deletion of a
PersistentVolumeClaimobject bound to aPersistentVolumecorresponding to this driver with adeletereclaim policy causes the sidecar container to trigger aDeleteVolumeoperation against the specified CSI endpoint to delete the volume. Once the volume is successfully deleted, the sidecar container also deletes thePersistentVolumeobject representing the volume.
원인 파악
위에서 조사한 내용에 따라서 external-provisioner에 대한 로그를 확인해 보았습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
> k logs -n kube-system ebs-csi-controller-67bbddfc9-zchxr -c csi-provisioner
I0326 05:22:00.602156 1 controller.go:1509] delete "pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720": started
I0326 05:22:00.602222 1 controller.go:1279] volume pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720 does not need any deletion secrets
E0326 05:22:00.602252 1 controller.go:1519] delete "pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720": volume deletion failed: persistentvolume pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720 is still attached to node ip-10-29-76-202.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal
W0326 05:22:00.602643 1 controller.go:989] Retrying syncing volume "pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720", failure 6
E0326 05:22:00.602669 1 controller.go:1007] error syncing volume "pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720": persistentvolume pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720 is still attached to node ip-10-29-76-202.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal
I0326 05:22:00.602705 1 event.go:298] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"PersistentVolume", Namespace:"", Name:"pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720", UID:"052bf861-a9e9-40e6-b36c-057bb0b6803f", APIVersion:"v1", ResourceVersion:"7111456", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Warning' reason: 'VolumeFailedDelete' persistentvolume pvc-3bd12eac-5eca-4cda-ae6c-c72e5a76d720 is still attached to node ip-10-29-76-202.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal
I0326 05:22:00.968493 1 controller.go:1366] provision "default/ebs-claim" class "ebs-sc": started
I0326 05:22:00.968940 1 event.go:298] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"PersistentVolumeClaim", Namespace:"default", Name:"ebs-claim", UID:"0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0", APIVersion:"v1", ResourceVersion:"7111525", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'Provisioning' External provisioner is provisioning volume for claim "default/ebs-claim"
I0326 05:22:13.036644 1 controller.go:1075] Final error received, removing PVC 0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0 from claims in progress
W0326 05:22:13.037419 1 controller.go:934] Retrying syncing claim "0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0", failure 3
E0326 05:22:13.037601 1 controller.go:957] error syncing claim "0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0": failed to provision volume with StorageClass "ebs-sc": rpc error: code = Internal desc = Could not create volume "pvc-0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0": could not create volume in EC2: WebIdentityErr: failed to retrieve credentials
caused by: InvalidIdentityToken: No OpenIDConnect provider found in your account for https://oidc.eks.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/id/ABC
status code: 400, request id: e027270f-f655-45a0-ba50-69ecb1809e5e
I0326 05:22:13.037230 1 event.go:298] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"PersistentVolumeClaim", Namespace:"default", Name:"ebs-claim", UID:"0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0", APIVersion:"v1", ResourceVersion:"7111525", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Warning' reason: 'ProvisioningFailed' failed to provision volume with StorageClass "ebs-sc": rpc error: code = Internal desc = Could not create volume "pvc-0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0": could not create volume in EC2: WebIdentityErr: failed to retrieve credentials
caused by: InvalidIdentityToken: No OpenIDConnect provider found in your account for https://oidc.eks.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/id/ABC
status code: 400, request id: e027270f-f655-45a0-ba50-69ecb1809e5e
E0326 05:22:13.037770 1 controller.go:1026] claim "0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0" in work queue no longer exists
E0326 05:22:21.038460 1 controller.go:1026] claim "0e86d2f9-8a0f-418a-80cd-3a04caec5fe0" in work queue no longer exists
InvalidIdentityToken: No OpenIDConnect provider found in your account for https://oidc.eks.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/id/ABC 에서 볼 수 있듯 OIDC 설정에 문제가 있었다는 것을 알 수 있었습니다.
해결
이는 제가 테라폼으로 여러 EKS 환경을 관리하면서 다른 OIDC 설정을 지우면서 발생했던 문제였습니다. 해당 OIDC 설정을 다시 해주고 DaemonSet의 Pod를 재실행했더니 잘 지워지는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
> k logs -n kube-system ebs-csi-controller-67bbddfc9-ntbsm -c csi-provisioner
W0326 05:38:26.823437 1 feature_gate.go:241] Setting GA feature gate Topology=true. It will be removed in a future release.
I0326 05:38:26.823503 1 feature_gate.go:249] feature gates: &{map[Topology:true]}
I0326 05:38:26.824399 1 csi-provisioner.go:154] Version: v3.6.3
I0326 05:38:26.824420 1 csi-provisioner.go:177] Building kube configs for running in cluster...
I0326 05:38:26.828914 1 common.go:138] Probing CSI driver for readiness
I0326 05:38:26.858228 1 csi-provisioner.go:230] Detected CSI driver ebs.csi.aws.com
I0326 05:38:26.858258 1 csi-provisioner.go:240] Supports migration from in-tree plugin: kubernetes.io/aws-ebs
I0326 05:38:26.861625 1 common.go:138] Probing CSI driver for readiness
I0326 05:38:26.864538 1 csi-provisioner.go:299] CSI driver supports PUBLISH_UNPUBLISH_VOLUME, watching VolumeAttachments
I0326 05:38:26.871538 1 controller.go:732] Using saving PVs to API server in background
I0326 05:38:26.871944 1 leaderelection.go:250] attempting to acquire leader lease kube-system/ebs-csi-aws-com...
I0326 05:38:42.852475 1 leaderelection.go:260] successfully acquired lease kube-system/ebs-csi-aws-com
I0326 05:38:42.852756 1 leader_election.go:178] became leader, starting
I0326 05:38:42.953118 1 controller.go:811] Starting provisioner controller ebs.csi.aws.com_ebs-csi-controller-67bbddfc9-ntbsm_99974c88-586f-40cf-afe8-68cfff66f7d4!
I0326 05:38:42.953175 1 volume_store.go:97] Starting save volume queue
I0326 05:38:43.058291 1 controller.go:860] Started provisioner controller ebs.csi.aws.com_ebs-csi-controller-67bbddfc9-ntbsm_99974c88-586f-40cf-afe8-68cfff66f7d4!
마치며
이번 글에서는 시간 관계상 CSI 가 무엇인지, CSI Driver는 어떤 구성 요소를 가지고 있는지에 대해서 간단하게 알아보았습니다.
다음에 기회가 된다면 좀 더 자세한 CSI Driver가 어떻게 동작하는지, 어떠한 과정을 거쳐서 볼륨을 관리하는지에 대해서 알아보도록 하겠습니다.